When your doctor prescribes digoxin, a cardiac glycoside used to treat heart failure and irregular heart rhythms like atrial fibrillation. Also known as digitalis, it works by strengthening heart contractions and slowing down certain electrical signals in the heart. But digoxin isn’t like most pills—you can’t just take it and forget it. It has a very tight line between helping you and harming you. Even a small overdose can cause serious problems, which is why serum digoxin level, the measured amount of digoxin in your blood is one of the most critical tests in heart medicine.
Why does this matter so much? Because digoxin affects your heart’s rhythm at the cellular level. Too little, and it won’t control your symptoms. Too much, and you could get nausea, vomiting, blurry vision, confusion, or even life-threatening heart rhythms. That’s why digoxin monitoring, the regular blood testing used to track how much of the drug is in your system isn’t optional—it’s standard care. Doctors don’t guess your dose based on weight or age alone. They rely on those lab numbers, especially if you’re older, have kidney issues, or take other meds like diuretics or antibiotics that can change how your body handles digoxin. digoxin toxicity, a dangerous buildup of the drug that can lead to arrhythmias or cardiac arrest happens more often than you think, and it’s usually preventable with simple blood tests.
You might wonder why your doctor doesn’t just adjust the dose based on how you feel. The truth is, you might not feel anything wrong until it’s too late. Some people with high digoxin levels feel fine until they suddenly develop a dangerous heartbeat. That’s why regular monitoring is non-negotiable. It’s not about being paranoid—it’s about being smart. And if you’re on digoxin, you’re not alone. Thousands of people rely on it every day, but only those who track their levels stay safe. Below, you’ll find real, practical guides from doctors and pharmacists on how to understand your test results, what to ask your provider, how to spot early warning signs, and what other medications might be interfering with your digoxin. This isn’t theory. These are the exact tools and insights used in clinics to keep people alive and well.
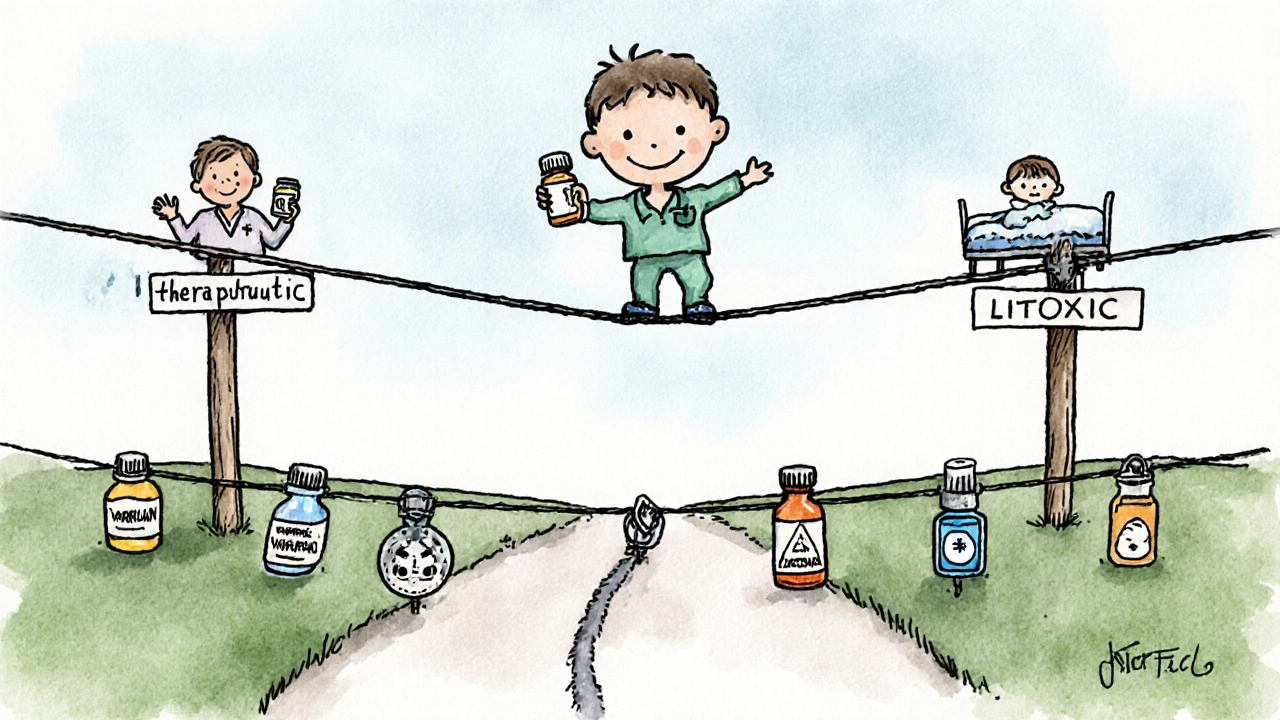
NTI drugs have a tiny margin between safe and toxic doses. Common examples include warfarin, lithium, digoxin, phenytoin, and tacrolimus. These require strict monitoring, careful dosing, and no brand switching without medical approval.
read more